Science & Technological Intervention for North East India (STINER) is a very ambitious, innovative and challenging assignment designed and conceived by Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region (MDoNER), Govt of India for the people of this region. The main goal of the project is to bring all the relevant proven technologies to the people of North Eastern Region (NER), more particularly to farmers and artisans community, so that the quality of their profession can be boost up through science and technological intervention. The relevant technologies will be exposed to farmers and artisans for exhibition and demonstration. Farmers can also use the facilities for processing their products to increase the shelf life of products for convenient storage and value addition. The facilities will also encourage budding entrepreneurs to start-up their business venture based on local agricultural resources. In addition to the technology mall, the hub will also have a quality testing laboratory for food and other products to support the growing demand of food processing industries, food processing shelf help groups...
More







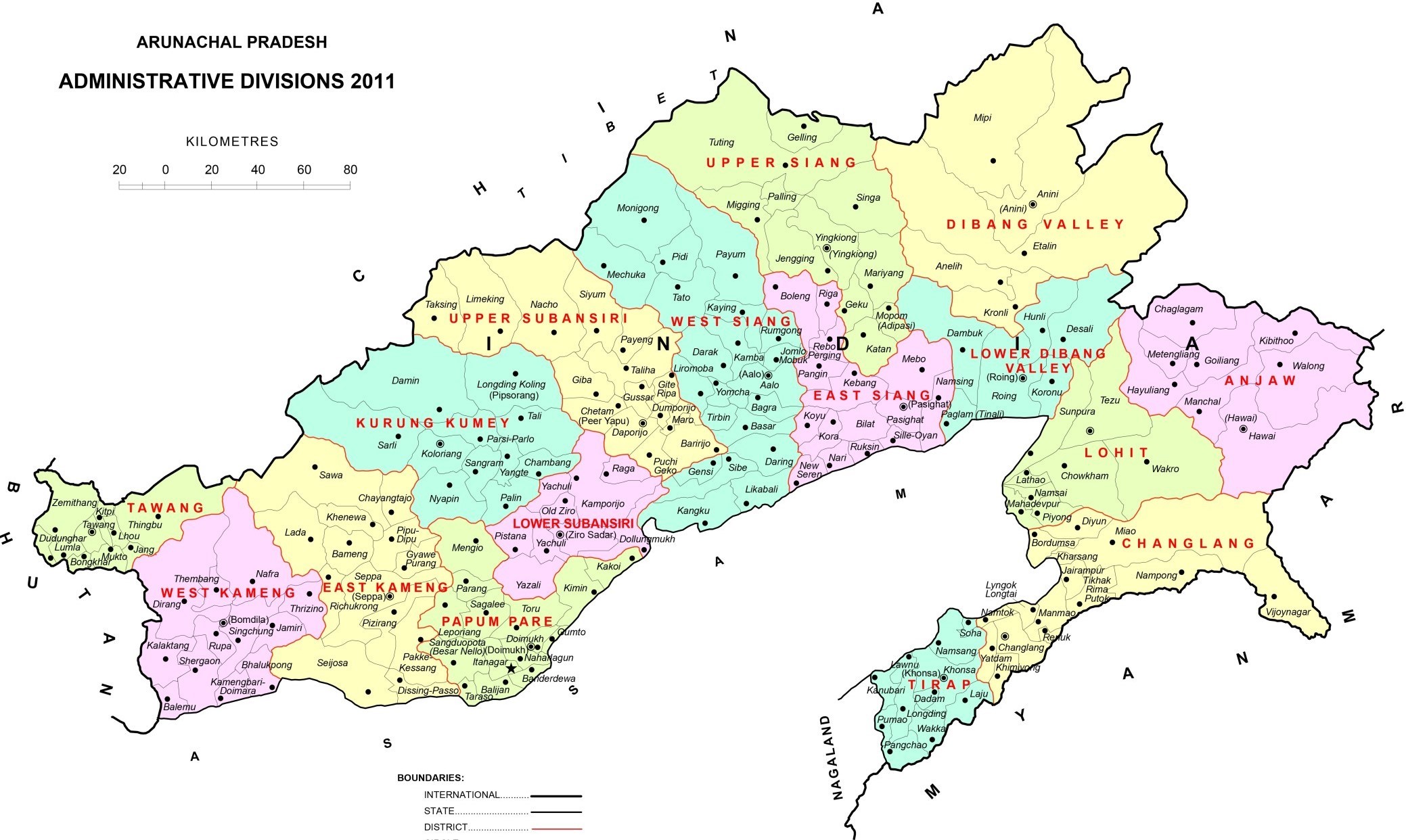
Arunachal Pradesh
The Land of Dawnlit Mountains
State Facts
Area: 83,743 km²
Population (2011): 1,382,611
Literacy: 66.95%
Capital: Itanagar
Established: 20 February 1987
Major crops and resources for economic upliftment
Arunachal Pradesh is basically an agricultural economy. Over 60% of the population is dependent on agriculture. Jhum cultivation is the main occupation of the farmers in Arunachal Pradesh and it has been practiced since past few decades. The state has approximately more than 500 indigenous species of medicinal and aromatic plants. The state has been producing 24755.38 metric tonnes (MT) of horticulture crops in the total cultivated area of 1487.95 × 103 hectares in every year. The main crops are Rice, Maize, Millet, Potato, Ginger, Mustard, Off season vegetables, Large cardamom. Cash crops like sugarcane and potato are also becoming popular. The agriculture in Arunachal Pradesh also comprise of production of few endemic vegetables such as sweet potatoes, brinjal, ginger, chillies, pumpkin, cucumber, and local cow pea. Fruit cultivation is also practiced in the agricultural sector of Arunachal Pradesh. The fruits that are cultivated include pineapple, apple, oranges, lemon, lichi, papaya, banana, plum, guava, cherries, peach walnut, and almond.
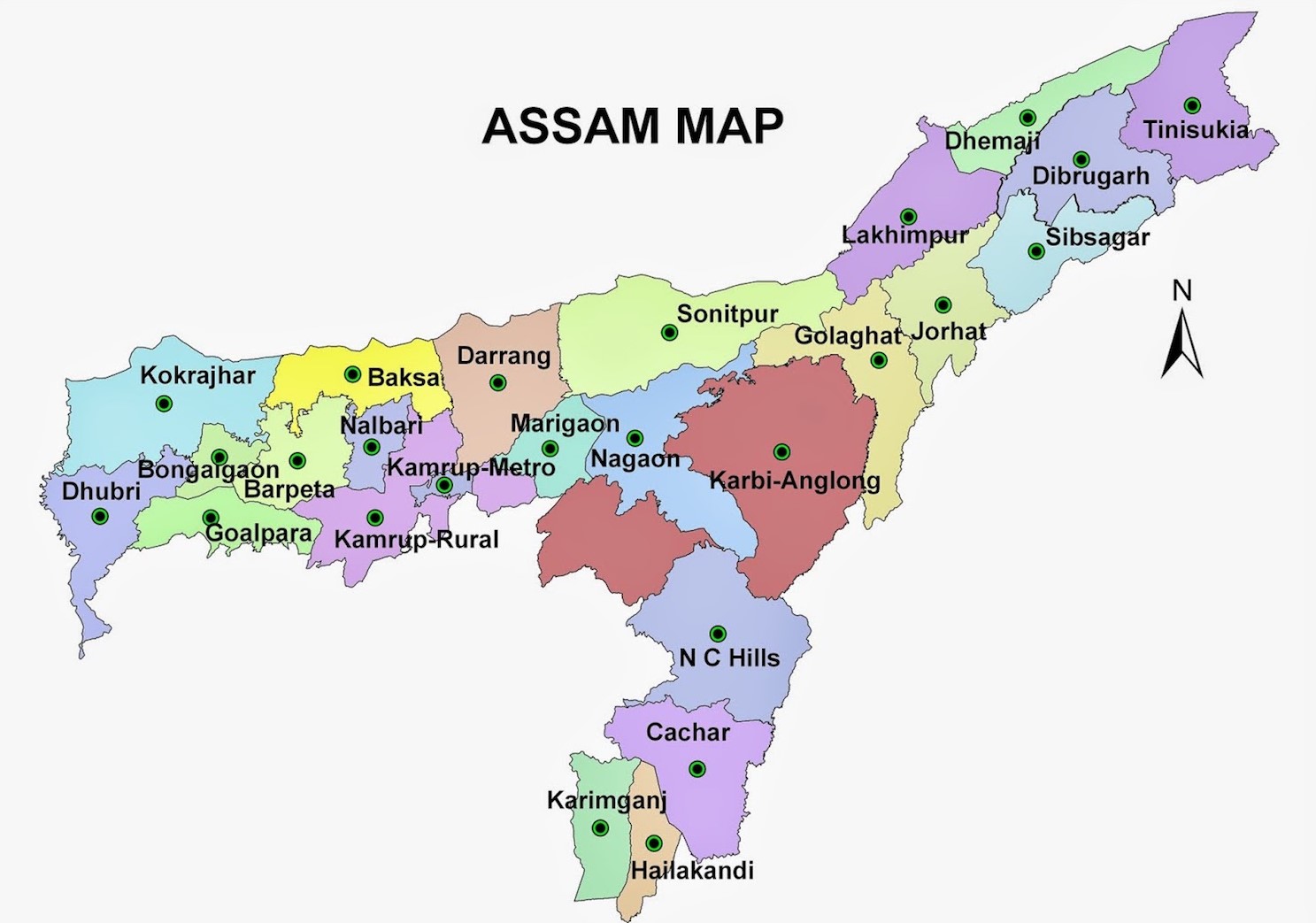
Assam
The Land of Red Rivers & Blue Hills
State Facts
Area: 78,438 Sq. km
Population (2011): 31,169,272
Literacy: 73.18%
Capital: Dispur
Established: 1912 (Assam Province - British India), 15 August 1947
Major crops and resources for economic upliftment
Assam is rich in natural resources. The natural resources of Assam may be classified under following heads – mineral, forest, water and agricultural resources. The State is one of the richest biodiversity zones in the world and consists of tropical rainforests, deciduous forests, riverine grasslands, bamboo orchards and numerous wetland ecosystems. Assam is abundant on mineral resources like coal, petroleum; limestone and natural gas. It is also the largest producer of crude oil in India. Other minor minerals include magnetic quartzite, kaolin, sillimanites, iron ore, clay and feldspar etc. Oil India Limited (OIL) is the second largest hydrocarbon exploration and production Indian public sector company with its operational headquarters in Duliajan, Assam, India under the administrative control of the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas. In Assam, agriculture makes the highest contribution to its domestic sectors, accounting for more than a third of Assam's income and employs about 69% of workforce. Assam has the single largest tea growing area in the world, constituting around one-seventh of the global tea production. Camellia assamica is the native variety of tea. The state accounts for over 50 per cent in the country’s overall tea production. Assam also accounts for fair share of India’s production of rice, rapeseed, mustard, jute, potato, sweet potato, banana, papaya, areca nut and turmeric. Assam is also a home to large varieties of citrus fruits, vegetables, leafy vegetables, useful grasses, herbs, spices, etc. which are mostly subsistence crops. Assam Silk denotes the three major types of indigenous wild silks produced in Assam-Golden Muga Silk, White Pat and warm Eri Silk.
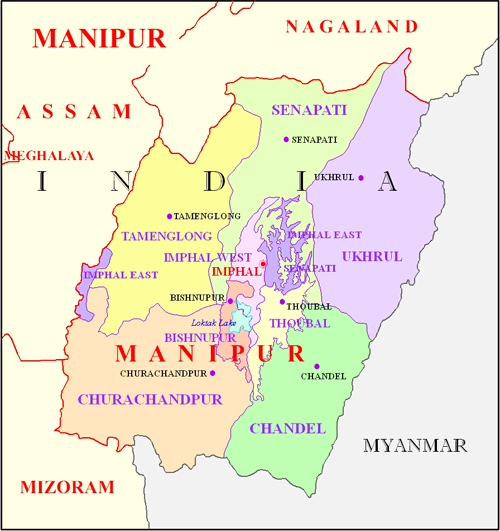
Manipur
The Jewel of India
State Facts
Area: 22327 sq.km
Population (2011): 2,388,634
Literacy: 68.87%
Capital: Imphal
Major crops and resources for economic upliftment
Agriculture is the main occupation of the people of Manipur. Agriculture sector contributes a major share to the total state domestic product and provides employment to about 22.13 percent (according to 2011 census) of the total workers in Manipur. Out of the total geographical area of the state, only 7.41 percent is used for cultivation. Of this total cultivated area, 52% is confined to the valley. Therefore, half of the total valley area, which accommodates 67% of the total population, is occupied for agriculture purposes. The agriculture practices in the state can be broadly categorized into two distinct types, viz., settled farming practiced in the plains, valleys, foothills, terraced slopes, etc. and shifting cultivation (Jhum) practiced on the hill slopes. The shifting cultivation leads to possible forest degradation in the foot hills and reduce the total sink potential across the state. There are 18 (eighteen) main crops which are cultivated during the two seasons in the state. Rice cultivation dominates all others crops. Some of the commercial crops grown in Manipur are cotton, kabrangchak, oilseeds and sugarcane which is very essential for enhancing the growth of agro-based industries in the state of Manipur. Common horticulture crops grown in the State are Kharif vegetables (French bean, Cucurbits, Tomatoes, Brinjal, Bhindi, Colocecia, Alocacia), Rabi vegetables (Cabbage, Cauliflower, Potato, Pea, Broad bean, Radish, Carrot, Broccoli, lettuce, Capsicum), Spices (Onion, Garlic, Chilli, Ginger, Turmeric, Hatkora) Fruits and Plantation Crops (Litchi, Cashew nuts, Wall nuts, Orange, Lemon, Banana, Pineapple, Passion fruit, Peach, Pear, Plum). The main categories of livestock reared in Manipur are cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat, pig, etc. Cattles and buffaloes provide motive power in wet cultivation. Rearing of pigs and poultry farming are found to be very important sources of income generating activities. The farmers in the state perform livestock rearing with a view of sustainable development & self-sufficiency in livestock products. But there is still a huge gap between demand and supply of these livestock products in the state.
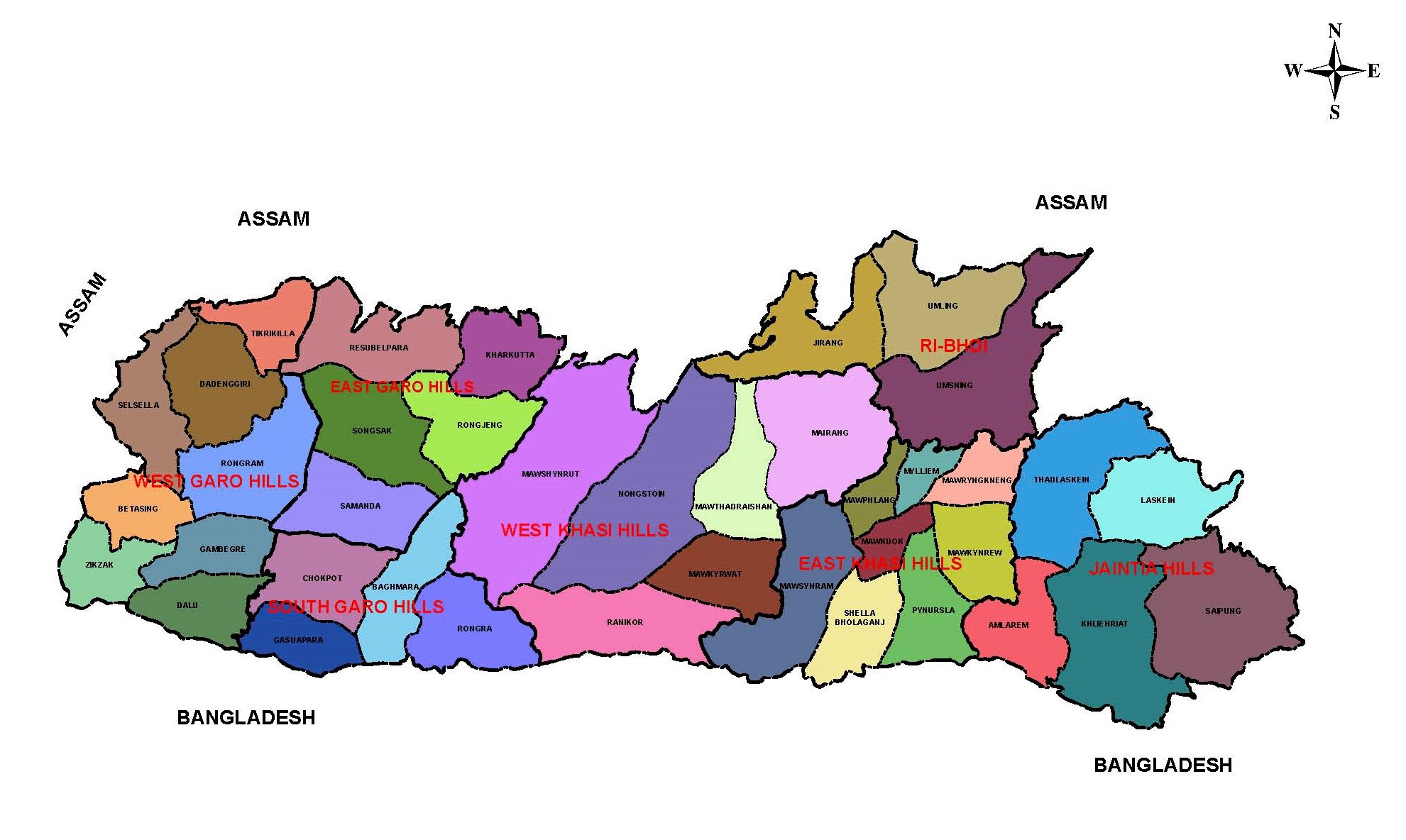
Meghalaya
The abode of clouds
State Facts
Area: 22,429 Sq. Km
Population (2011): 29,64,001
Literacy: 75.48 %
Capital: Shillong
Established: 21 January 1972
Major crops and resources for economic upliftment
Meghalaya, one of the most beautiful State in the country. Nature has blessed her with abundant rainfall, sun-shine, virgin forests, high plateaus, tumbling waterfalls, crystal clear rivers, meandering streamlets and above all with sturdy, intelligent and hospitable people. Shillong, the capital of Meghalaya is located at an altitude of 1496 metres above sea level. Agriculture is the main occupation of the people of Meghalaya. Of the total agricultural land in Meghalaya, 62% is used for food grains, 25% for cash crops, 9% for horticultural crops and the rest 4% is used for raising miscellaneous crops. The state offers scope for cultivation of a wide variety of agricultural crops because of highly diversified topography, altitude and climatic conditions. Rice is the most important food crop and occupies about 44% of the total agricultural land. Maize is the next important agricultural food crop of Meghalaya. It is grown in about 8% of the cropped area and cultivated mainly in the plains of Garo hills, Mairang, Mawphlang and Laskeiñ block of Jaiñtia hills. Cotton, Jute, Mesta are the important fibre crops grown in the State. These crops have been the traditional cash crops of Garo Hills. Besides the major food crops of rice and maize, the state is renowned for its horticultural crops like Orange, Pineapple, Lemon, Guava, Litchi, Jackfruit and Bananas; and fruits such as Plum, Pear and Peach.
MIZORAM
The Jewel of India
State Facts
Area: 21081 Sq. km
Population (2011): 1,091,014
Literacy: 91.58%
Capital: Aizawl
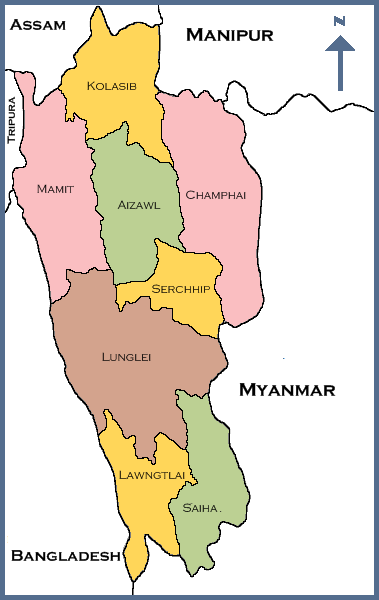
Major crops and resources for economic upliftment
About 80 per cent of the people of Mizoram are engaged in agricultural related activities. The main agriculture practices are Jhum or Shifting cultivation. Mizoram has the potential of 6.30 lakh hectares land for cultivation of horticulture crops out of the total estimated land of 21 lakh hectares. But, the actual utilization of land for horticultural crop is only around 4127.6 hectares, which is only 6.55 per cent of the estimated potential area. The indication is clear that there is a huge scope for boosting up the horticultural crops to flourish in Mizoram. Mandarin Orange, Banana, Passion Fruit, Grapes, Hatkora, Pineapple, Papaya, etc., are the main horticultural crops cultivated at Mizoram. Flowers like Anthurium, Bird of Paradise, Orchid, Chrysanthemum, Rose and other subsidiary seasonal flowers are also grown in the state of Mizoram. Spices like Ginger, Turmeric, Black Pepper and Bird's eye Chillies are grown at large areas of land estimated at 22470 ha with total production of major spices of 59620 MT (Anonymous, 2016). People have also started extensive cultivation of oil palm, medicinal and aromatic plants. Mizoram is one of the highest producers of ginger amongst Indian states. The total production of ginger was about 28400 metric tonnes (Anonymous2015 & Das 2016). Similarly, 8200 MT of turmeric and 24700 MT of chilli produced in the year of 2015-2016, which was quite high as compared to other states of India. Jhum and sugarcane were the major agricultural crop produced in 2014-2015 with total production 23,583 MT and 44,257 MT respectively. Oilseeds, maize and pulses are the other agricultural product produces in large quantities in Mizoram. Most suitable horticultural crops are produced during 2015-2016 are mandarin Orange/Orange (41 MT), banana (141 MT), passion fruit, pineapple (33 MT). There are some medicinal and Aromatic plants are also grown in Mizoram like Stevia, Achla, Aloevera.
Nagaland
The land of festivals
State Facts
Area: 16579 Sq. km
Population (2011): 19,80,602
Literacy: 80.11%
Capital: Kohima
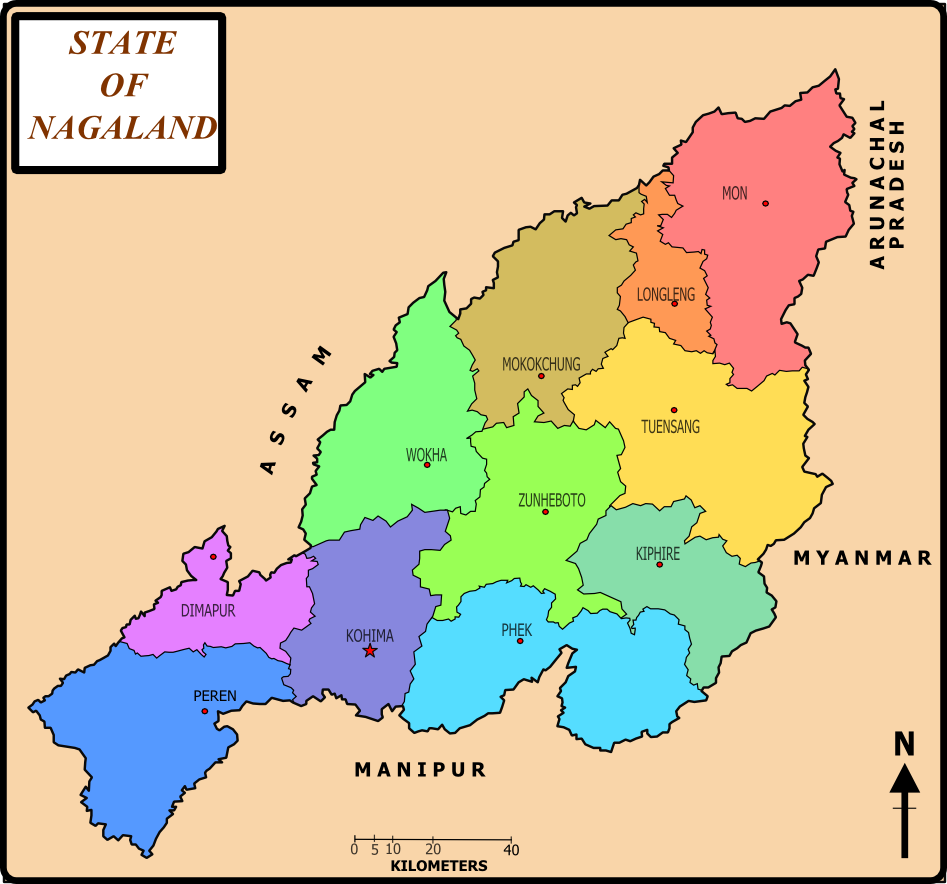
Major crops and resources for economic upliftment
The state has considerable resources of natural minerals, petroleum and hydropower. It has unexploited reserves of around 600 million metric tonnes (MT) of crude oil and more than 20 MT of hydrocarbon. Moreover, the state has 315 MT of coal reserves and 1,038 MT of limestone reserves. Nagaland’s estimated hydropower generation potential is 1,574 megawatt (MW), while the state has a total installed power generation capacity of 154.87 MW. The economy of the Nagaland is based mostly on agriculture. The agro-climatic conditions in Nagaland provide commercial opportunities for floriculture and horticulture. The state has 650 indigenous species of medicinal and aromatic plants. The state is estimated to have the potential to produce 15,000 MT of honey and 100 MT of wax, which together could generate around US$ 100 million annually. Moreover, the production of honey during 2016-17 was recorded to be 0.45 thousand tones. Nagaland has basically an agricultural economy. Over 70% of the population is dependent on agriculture. The main crops are rice, millet, maize and pulses. Cash crops like sugarcane and potato are also becoming popular. Coffee, cardamom and tea are grown as plantation crops in Nagaland. Rice is the dominant crop and also the staple diet of the people. Of the gross cropped area under food grains, rice accounts for about 84.4%. Oil seeds are also an important crop. It includes Rapeseed, mustard etc. Coffee cardamom and tea are grown as plantation crops in Nagaland. Principal crops are Arums, yams, millet, maize, potatoes and sugarcane. Vegetable crops are melon, cucumbers, spinach leaf, mustard, onion, chillies, carrots, tomatoes, brinjal etc. The two methods of cultivation among the Naga tribes are jhuming and terrace cultivation. The area under jhum cultivation is about 87.339 hectares and under terraced cultivation is about 62,091 hectares.
Sikkim
Small but Beautiful
State Facts
Area: 7096 Sq. km
Population (2011): 610,577
Literacy: 82.2%
Capital: Gangtok

Major crops and resources for economic upliftment
Agriculture is the main stay of rural population of Sikkim. The major agricultural and horticultural crops of Sikkim are Rice, Maize, Finger Millet, Barley, Wheat, Urd, Pea, Soyabean, Mustard, Potato, Sweet Potato, Large Cardamom, Chilly, Turmeric, Coriander, Ginger, Mandarin, Banana, Papaya, Litchi, Guava, Jack Fruit, Brocolli, Iskus, Tomato, Cauliflower, Pumpkin, Tree Tomato, Brinjal, Carrot, Radish, Cabbage. Sikkim accounts for the largest share of cardamom production in India, and is the world's second largest producer of the spice after Guatemala. Sikkim achieved its ambition to convert its agriculture to fully organic over the interval 2003 to 2016, the first state in India to achieve this distinction. It is also among India's most environmentally conscious states, having banned plastic water bottles "in any government functions and meetings" and polystyrene products (throughout the state). Horticultural activities in the State comprise of activities that aim at promoting production of fruits such as Sikkim mandarin, pear, kiwi, papaya, banana as well as traditional vegetables such as bean, garden pea and other vegetables like tomato, cole crops, radish, etc. Other cucurbits such as chayote, potato and spice crops like large cardamom, ginger, turmeric, cherry pepper and flowers such as cymbidium orchids, rose, lilium, gladioli, anthurium, carnation, gerbera, alstroemeria and zantedeschia. The activities relating to promotion of non- traditional practices like bee keeping, mushroom cultivation, plantation of bamboo and medicinal plants have been intensified to add greater diversification. The significance of horticulture in improving land use, promoting crop diversification, generating employment and providing nutritional security to people has been recognized by and large by common man, general public, framers and programme implementers. Hence, horticulture features as an important area in the overall policy framework for development in the State.
TRIPURA
A place of satiety
State Facts
Area: 10486 Sq. km
Population (2011): 36,71,032
Literacy: 87.75 %
Capital: Agartala
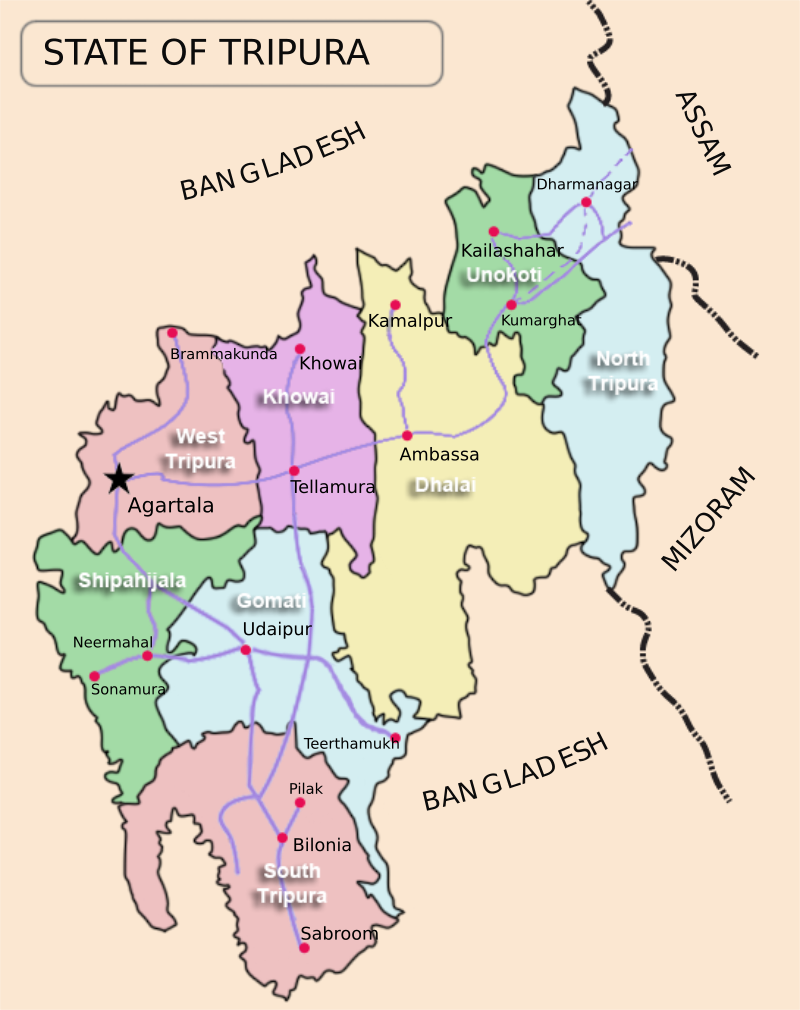
Major crops and resources for economic upliftment
The industrial sector of the state continues to be highly underdeveloped: brickfields and tea industry are the only two organised sectors. Tripura has considerable reservoirs of Natural gas. According to estimates by Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC), the state has 400 billion metres3 reserves of natural gas, with 16 billion metres3 is recoverable. ONGC produced 480 million metres3 natural gas in the state, in 2006-07. In 2011 and 2013, new large discoveries of Natural gas were announced by ONGC. Besides Natural Gas, Tripura is enriched in Glass sands of 3,62,832 Tons, Limestone of 990.00 Tons and Plastic Clay 1.73 Million Ton.




© Copyright CSIR-NEIST, Jorhat-6, Assam. All Rights Reserved