Manipur
The Jewel of India
State Facts
Area: 22327 sq.km
Population (2011): 2,388,634
Literacy: 68.87%
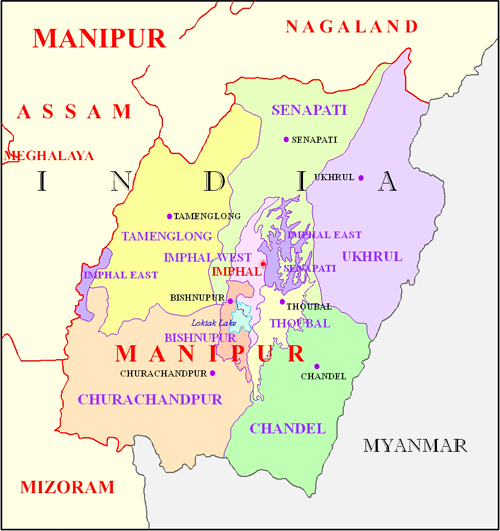
Capital: Imphal
Major crops and resources for economic upliftment
Agriculture is the main occupation of the people of Manipur. Agriculture sector contributes a major share to the total state domestic product and provides employment to about 22.13 percent (according to 2011 census) of the total workers in Manipur. Out of the total geographical area of the state, only 7.41 percent is used for cultivation. Of this total cultivated area, 52% is confined to the valley. Therefore, half of the total valley area, which accommodates 67% of the total population, is occupied for agriculture purposes. The agriculture practices in the state can be broadly categorized into two distinct types, viz., settled farming practiced in the plains, valleys, foothills, terraced slopes, etc. and shifting cultivation (Jhum) practiced on the hill slopes. The shifting cultivation leads to possible forest degradation in the foot hills and reduce the total sink potential across the state. There are 18 (eighteen) main crops which are cultivated during the two seasons in the state. Rice cultivation dominates all others crops. Some of the commercial crops grown in Manipur are cotton, kabrangchak, oilseeds and sugarcane which is very essential for enhancing the growth of agro-based industries in the state of Manipur. Common horticulture crops grown in the State are Kharif vegetables (French bean, Cucurbits, Tomatoes, Brinjal, Bhindi, Colocecia, Alocacia), Rabi vegetables (Cabbage, Cauliflower, Potato, Pea, Broad bean, Radish, Carrot, Broccoli, lettuce, Capsicum), Spices (Onion, Garlic, Chilli, Ginger, Turmeric, Hatkora) Fruits and Plantation Crops (Litchi, Cashew nuts, Wall nuts, Orange, Lemon, Banana, Pineapple, Passion fruit, Peach, Pear, Plum). The main categories of livestock reared in Manipur are cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat, pig, etc. Cattles and buffaloes provide motive power in wet cultivation. Rearing of pigs and poultry farming are found to be very important sources of income generating activities. The farmers in the state perform livestock rearing with a view of sustainable development & self-sufficiency in livestock products. But there is still a huge gap between demand and supply of these livestock products in the state.




© Copyright CSIR-NEIST, Jorhat-6, Assam. All Rights Reserved